I now how people love to see all the pictures from space and hear all the stories of the wonders that James Webb has discovered. DAILY we see reports that James Webb is completely shattering everything we know about our Universe.
Makes for great press. People eat it up. BUT IT IS SOLID BULLSHIT. All created out of the imagination of AI using lights, smoke and mirrors. I hate to break anyone’s bubble. And, if you want to go on buying into their artificial reality, I won’t hold it against you. Do whatever you CHOOSE. Just remember choices always have consequences, though they may not manifest immediately, they come.
The truth is we live under a firmament. Created by GOD ALMIGHTY. Nothing and no-one has broken through it. Space is water above the firmament. God separated the waters above from the waters below. There are no galaxies “OUT THERE” at least none that we can know or explore. Unless or until GOD reveals them.
The sun, moon and stars, including the wondering stars are all directly above our heads and within the firmament. GOD set them there as lights and as signs FOR US. So that we can know the TIMES and the SEASONS.
THERE ARE NO SATELLITES circling “the globe”. There is NO GLOBE. The earth is flat and stationary and cannot be moved. The sun, moon and stars circumnavigate the surface of the earth in a circle. Well, kinda more like a spiral.
Our GPS and our Internet is not provided for us via Satellite. When you really understand what they have been building around us it should make you angry.
MY DEFINITION OF A LOON: ANYONE WHO STILL BELIEVES WHAT MAINSTREAM NARRATIVE, whether it is coming from the Media, Technology Giants, the Medical Industry, Think Tanks, Universities, The Pope, the “CHURCH”, Politicians or any other Mainstream Organization.
spacer
 |
Loon LLC
Internet company
|

spacer
Description
Loon LLC was an Alphabet Inc. subsidiary working on providing Internet access to rural and remote areas. The company used high-altitude balloons in the stratosphere at an altitude of 18 km to 25 km to create an aerial wireless network with up to 1 Mbit/s speeds. Wikipedia
 |
Alphabet Inc.
Multinational conglomerate company
|
Description
Alphabet Inc. is an American multinational technology conglomerate holding company headquartered in Mountain View, California. It was created through a restructuring of Google on October 2, 2015, and became the parent company of Google and several former Google subsidiaries. Wikipedia
Aug 14, 4:00 PM EDT – Disclaimer



is for Google
As Sergey and I wrote in the original founders letter 11 years ago, “Google is not a
conventional company. We do not intend to become one”

Spacer
|
|
X
Research and development company
|
Description
X is an American semi-secret research and development facility and organization founded by Google in January 2010. X has its headquarters about a mile and a half from Alphabet’s corporate headquarters, the Googleplex, in Mountain View, California. Wikipedia
 |
Inside Google’s Wildly ambitious internet balloon project
spacer


 |
 |
Taara

Bringing the Internet to underserved locations
The Taara team is implementing 20 Gbps connectivity over distances up to 20 km with units that are fast and easy to deploy. The team is working with telcos, internet service providers (ISPs), and governments around the world to significantly accelerate the deployment of the extensive, high-throughput networks necessary to support the future of the web.
spacer
SPACE LASERS PEW PEW —
Google spinoff Aalyria salvages Project Loon technology for the US military
Loon’s laser communications and networking software get new life as Aalyria.
A pair of reports from CNBC and Bloomberg are detailing a new Google connectivity spinoff called “Aalyria.” The new company sounds like it’s taking the canceled Project Loon technology, packaging it up under a new brand name, and spinning it out from Alphabet as an independent company, where it will hopefully survive in the wilderness. The company is apparently going public today, complete with a spiffy new website.
|
Allyria Name Meaning |
| Allyria meaning Alyria is of Dominican Republic origin and means “Leader of men”. A user from Mississippi, U.S. says the name Alyria means “A person”. The name Allyria has Fire element. Mars is the Ruling Planet for the name Illyria . The name Allyria having moon sign as Aries is represented by The Ram and considered as Cardinal Source |
spacer
Project Loon was a Google/Alphabet company for eight years and wanted to provide Internet for low-connectivity areas with flying cell towers suspended overhead by weather balloons. It’s sort of the same idea as a low Earth orbit satellite, but rather than a satellite in space, these balloons were only 20 km in the air. Besides needing to constantly navigate the varying atmospheric airways, Loon balloons have to be continually recovered and relaunched to maintain a steady stream of overhead balloons. Besides being a reference to the big weather balloons, the name “Loon” was chosen as a nod to how infeasible the idea sounds. Eventually that infeasibility proved to mostly just be a money problem, and Google shut down Loon in 2021, saying it wasn’t a “long-term, sustainable business.”

Aalyria’s two big technologies are “Tightbeam” and “Spacetime.” Tightbeam seems born out of the Project Loon research and uses a laser to communicate with satellites. Project Loon was using lasers for intra-balloon communication, and now Aalyria promises to beam data to space, terrestrial, and airborne targets “at rates faster than any other solutions available today and covering greater distances than previously imagined.” SpaceX, which is probably Aalyria’s biggest competitor in the field of bringing Internet to low-connectivity spaces, already uses lasers for satellite-to-satellite communication.
Spacetime is “a software platform for orchestrating networks across land, sea, air, space and beyond.” Aalyria’s site says the software is for “orchestrating networks of ground stations, aircraft, satellites, ships, and urban meshes.” Spacetime “optimizes and continually evolves the antenna link scheduling, network traffic routing, and spectrum resources—responding in realtime to changing network requirements” and is “designed for interoperability with legacy, hybrid space, 5G NTN and FutureG network architectures.”
Loon had to manage a loosely tied-together network of constantly moving (and crashing) balloons, and building an Internet service on top of that unstable infrastructure probably required robust routing software. Bloomberg says: “The key technology behind Spacetime is algorithms that predict, for example, when a plane is about to lose its connection with a given satellite or ground station and then direct a new signal toward the plane without missing a beat.”
CNBC reports that Alphabet retains a minority stake in the new startup, and Alphabet “transferred nearly a decade’s worth of intellectual property, patents and physical assets, including office space, to Aalyria.” Aalyria will need to survive on funding from places other than Alphabet, and it also has funding from the founders of Accel, J2 Ventures, and Housatonic.

The startup seems to have a heavy US military focus right now, including an $8.7 million “commercial contract” with the US Defense Innovation Unit. The “contracted by” section of Aalyria’s website shows the logos for the US Space Force, Space Warfighting Analysis Center, US Air Force, and US Special Operations Command. The company’s advisory board includes former Deputy Defense Secretary Robert O. Work and Former US Space Force Chief Innovation & Technology Officer Kim Crider.
The US Defense Innovation Unit put out a press release about the Aalyria contract back in July, saying, “A fully networked battlespace has been the dream of commanders for decades, but is now finally within reach.” For now, the initial goals are “on-demand or near-real-time satellite imagery,” “theater-wide tracking” of a battle, and “reliable broadband Internet at remote forward operating bases.”
spacer
THE LOON PROJECT TELLS US A LOT! Most importantly, it verifies that we are not living on a spinning ball!
SPACE X Above a FLAT EARTH!
spacer
THE LOON PROJECT
spacer
PROJECT LOON PROVES THERE ARE NO SATELLITES IN SPACE
spacer
Internet Balloons Connecting the World/Tech it Out
spacer
“GOOGLE’S PROJECT LOON PROVES THE FLAT EARTH”
spacer
The earliest military application of a balloon is often credited to Zhuge Liang, a well-known war strategist in dynastic China. That was in the 3rd century, when he used kerosene-doused cloth to propel a sky lantern that alerted allies in neighboring cities of a looming attack.
In the almost two thousand years since, balloon technology advanced and was used increasingly for reconnaissance missions during wars in the 19th and early 20th centuries, particularly during the Cold War. But the advent of satellites and drones rendered spy balloons mostly obsolete.
Until recently, it seems.
On Wednesday, a mysterious white orb was spotted floating above Billings, Montana, and U.S. security officials suspected it almost certainly to be a Chinese military surveillance balloon. The sighting sent politicians on high alert: House Speaker Kevin McCarthy called it a “brazen disregard for U.S. sovereignty” and the Pentagon scrambled fighter jets to deal with it. However, even though the balloon was hovering over sensitive sites, including a field housing U.S. nuclear missiles, the Biden administration decided not to shoot it down just yet, as officials advised that it doesn’t pose a threat for now but its debris might.
“We have no intention to violate the territory or airspace of any sovereign country,” Mao Ning, a spokesperson for China’s foreign ministry said at a briefing on Friday. “We are gathering and verifying the facts. We hope both sides can handle the matter together in a cool-headed and prudent manner.” The ministry later admitted that the balloon was from China but described it as a “civilian airship used for research, mainly meteorological, purposes” that was steered off course by the wind. (Same Bullshit our government hands out, coming back on them must be irritating!! lol)

How unusual are spy balloons these days?
This isn’t the first time in recent history that a balloon from China has been spotted by foreign security officials.
After the sighting this week, the U.S. Department of Defense said in a statement: “Instances of this kind of balloon activity have been observed previously over the past several years.”
Last February, authorities in Taiwan said they discovered weather balloons deployed by the Chinese People’s Liberation Army floating above the self-governing island that China claims as its territory. While some speculated the balloons could be used for surveillance, officials in Taipei accepted that they were meant for meteorological observations only.
China has been developing new balloon surveillance technology for years, but it’s not the only country to do so.
Last May, Politico reported that the Pentagon spent around $3.8 million on balloon projects over the past two years and planned to spend more than $27 million on the inflatable tech in fiscal year 2023. The balloons, according to the report, will collect data and transmit information to aircraft and may eventually be used to scan for hypersonic weapons developed by China and Russia.
Why use balloons when satellites exist?
China has an extensive satellite network. In a Nov. 2022 report, the Defense Department said China’s intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance-capable (ISR) satellite fleet had more than 260 systems, second only to the U.S., as of the end of 2021. A senior defense official noted on Thursday that, for China, the balloon flying over Montana “has limited additive value from an intelligence collection perspective.”
Yet even with satellite technology surpassing some abilities of balloons, James Char, a research fellow with the China Programme at the S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies in Singapore, tells TIME that spy balloons have some operational advantages. For example, balloons can weather extreme conditions, he says, and are less expensive to deploy and operate compared to satellites. Chinese Academy of Science scholars found in 2020 that, despite harsh environments at more than 68,000 feet above ground, “the high-altitude balloon has long endurance time, which can achieve sustained and wider coverage for regional observation and detection.”
“It is harder to be spotted by radar as well, given the fact that they’re simpler in terms of technology,” Char adds. U.S. officials admitted the balloon flying over North America this week was first spotted by civilians on a plane.
High-altitude balloons can also be “trucks for any number of platforms, whether it be communication and data link nodes, ISR, tracking air and missile threats — and without the predictable orbits of satellites,” Tom Karako, senior fellow for the International Security Program and director of the Missile Defense Project at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, told Politico.
And though the technology is old, says Bec Shrimpton, director at the Australian Strategic Policy Institute, balloons can complement surveillance technology in orbit, while they can be built and deployed at a fraction of the cost. According to a 2020 analysis in defense publication Armada International, the development, launch, operation, and insurance of a single satellite can cost up to $300 million.
Another potential edge for balloons, Shrimpton tells TIME, is how unlikely defense officials may have been prepared for it to be used, especially by China. “It’s probably better because it’s unexpected,” she says. “It’s not that we haven’t seen this before, but we are expecting far more from Chinese surveillance efforts.”
spacerspacer
WHERE DO FIBRE OPTICS COME IN TO THEIR PLAN??? Let’s take a look and see what we find.
spacer
Fibre-optic Link Around the Globe

Logo from 2003
|
|
| Industry | Telecommunication |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1999 |
| Owner | Global Cloud Xchange |
Fibre-optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG) is a 28,000-kilometre-long (17,398 mi; 15,119 nmi) fibre optic mostly-submarine communications cable that connects the United Kingdom, Japan, India, and many places in between. The cable is operated by Global Cloud Xchange, a subsidiary of RCOM.[1] The system runs from the eastern coast of North America to Japan.[2] Its Europe-Asia segment was the fourth longest cable in the world in 2008.[3]
The Europe-Asia segment was laid by Cable & Wireless Marine in the mid-1990s, and was the subject of an article in Wired magazine in December 1996 by Neal Stephenson.[2]
Description
The FLAG cable system was first placed into commercial service in late 1997.[4] FLAG offered a speed of 10 Gbit/s, and uses synchronous digital hierarchy technology. It carries over 120,000 voice channels via 27,000 kilometres (16,777 miles; 14,579 nautical miles) of mostly undersea cable. FLAG uses erbium-doped fibre amplifiers, and was jointly supplied by AT&T Submarine Systems and KDD-Submarine Cable Systems. Its design, development, installation, and service conformed to ISO 9000 quality standards. FLAG provided a link between the European end of high-density transatlantic crossings and the Asian end of the transpacific crossings.[5]
FLAG includes undersea cable segments, and two terrestrial crossings. The segments can be either direct point-to-point links, or multi-point links, which are attained through branching units. At each cable landing point, a FLAG cable station is located. The total route length exceeds 27,000 kilometres (16,777 miles; 14,579 nautical miles), and comprises 1,020 kilometres (634 miles) of terrestrial crossings. Approximately 6,600 kilometres (4,101 miles; 3,564 nautical miles) of the submerged cable is buried 1 metre (3 feet 3 inches) below the sea bed. Cable burial was performed by either a submersible plough as the cable was laid, or jetting the laid cable into the sea bed via remotely operated vehicles (ROVs).[5]
Over several years, the route evolved as new branches and feeder systems were considered and realized. FLAG includes two terrestrial crossings, one in Egypt, and the other in Thailand. Each of these land crossings is totally duplicated on fully different routes. As a result, any fault within one route will cause automatic protection switching to the other route within a time period of less than 50 ms.[5]
Like other global undersea networks, FLAG uses erbium-doped fibre amplifiers (EDFAs). EDFAs boost the optical signals instead of the optical/electrical conversion, which is generally used in regenerative technology. These optical amplifiers use short, gain-specific lengths of fibre which are doped with erbium ions, and spliced in-line with the transmission fibre. The signal power is amplified by pumping the erbium-doped fibre (EDF) with 1,480 nm laser light which is attached through an optical coupler. The majority of the repeater components are passive. These include EDF, fused-fibre optical couplers and optical isolators. Active components include laser pump assemblies, and associated controls. The total number of components within the repeater is lesser than that of regenerative systems.[5]
The FLAG terrestrial crossings do not contain repeaters for reliability reasons. The terminal stations in land crossings use optical amplifiers, high performance transmitter / receivers, and forward error correction to cross the large distances without repeaters. Amplification at the terminal output provides output signal power as high as +17 dBm, and optical amplification at the receiver improves the receiver sensitivity as much as 8 dB.[5][clarification needed]
The route between Alexandria and Cairo is 223 kilometres (139 miles) long, and hence requires remote pumping in order to meet performance requirements. Remotely pumped amplifiers can be regarded as repeaters without active modules. This technology comprises short lengths of EDF spliced into the land cable. The erbium-doped sections are situated within the cable span, and are pumped by 1,480 nm pump lasers which are based at the station.[5]
An upgrade to the network was announced in 2006, when the acronym was expanded to “Fibre Loop Across Globe” (FLAG).[6][clarification needed]
Segments and landing points
Cable landing points are:
Europe Asia[edit]
FLAG Europe Asia (FEA) was the first segment opened for commercial use on 22 November 1997.[4][7]
|
|
Atlantic
The FLAG Atlantic 1 (FA-1) segment became operational in June 2001.[8] It was constructed as a joint venture between a FLAG Atlantic subsidiary of the parent company FLAG Telecom Holdings, and GTS Transatlantic. Alcatel Submarine Networks laid the undersea portion, and the entire cost was estimated at $1.1 billion.[4][9]
|
|
In March 2013, an upgrade for the southerly link was announced to up to 100 Gbit/s, with equipment from Ciena.[10]
FLAG Alcatel-Lucent Optical Network
The FLAG Alcatel-Lucent Optical Network (FALCON) cable system, connecting India and several countries in the Persian Gulf, became operational in September 2006.[11] It has landing points in:[12][13]
|
|
There is an additional segment, listed as part of FALCON, but not directly connected. It has landing points in:[12]
|
In 2006, Kenya Data Networks announced plans for a spur from Yemen to Mombasa.[14]
FLAG North Asia Loop / Tiger
FLAG North Asia Loop (FNAL) / Tiger became operational in stages, with the final stages completed in 2002.[15] The FNAL landing points are:[16]
West of Mumbai, FLAG has a capacity of 80 Gbit/s.
The segment between Lantau, Hong Kong, and Busan, South Korea was broken by the 2006 Hengchun earthquake.
See also
- Reach North Asia Loop (RNAL), cable network developed jointly by Reach and FLAG Telecom
- List of international submarine communications cables
Other cable systems following a substantially similar route to FLAG Europe-Asia (FEA) are:
|
spacer
spacer
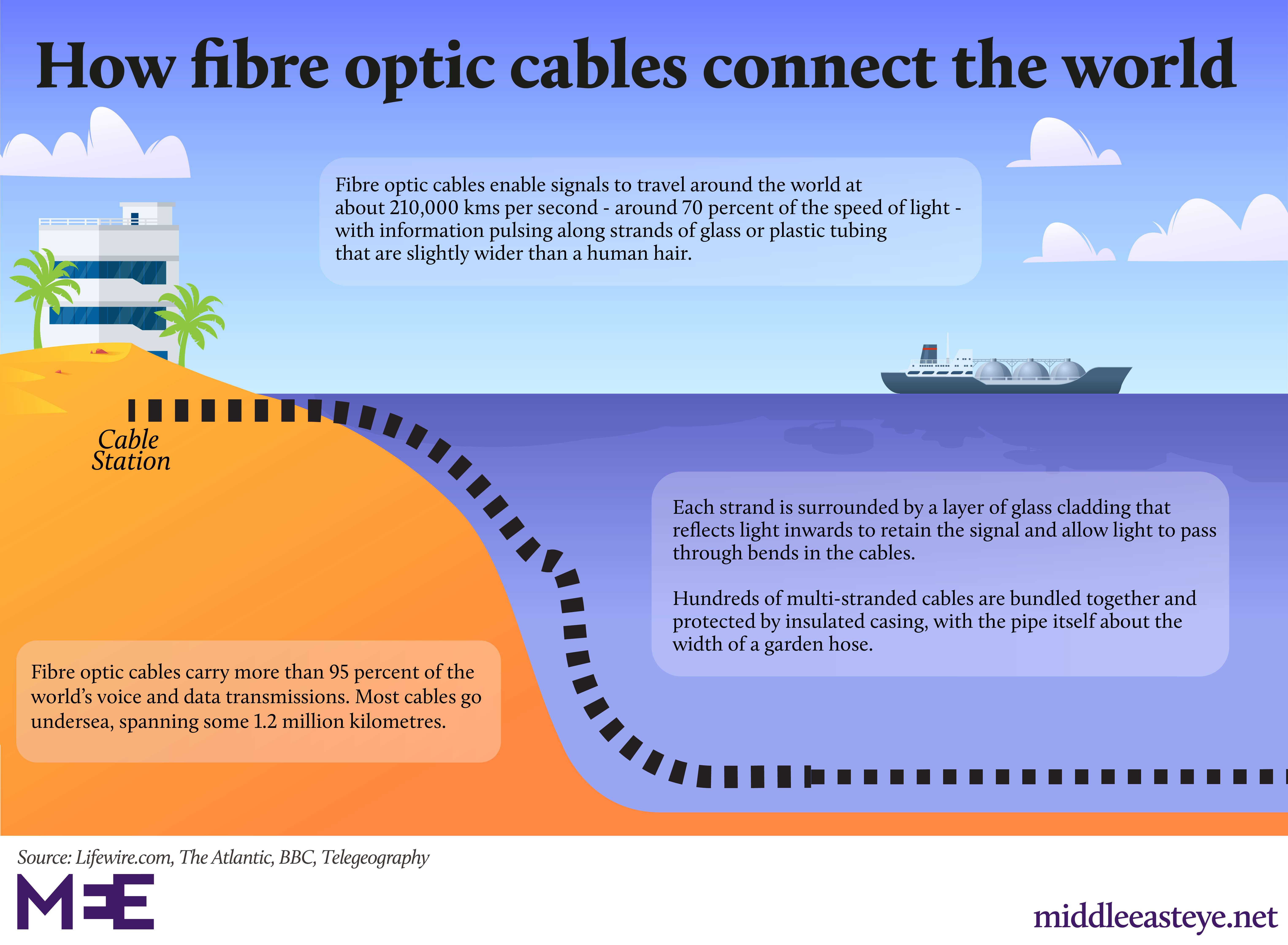
Fiber-based networks make up the majority of the internet’s backbone. Fiber-optic subsea cables spanning thousands of miles connect continents together, exchanging data at nearly the speed of light. Meanwhile, the massive data centers that host all of our cloud-based applications also rely on fiber connections. Increasingly, these fiber connections are making their way directly into peoples’ homes, providing them with fast, reliable internet. But, only 43% of U.S. households have access to a fiber internet connection.
“In some instances, particularly in rural areas and very challenging geographies, it can be prohibitively expensive to to deploy fiber and it can be very expensive for households to pay for it,” says Julija Jurkevic, a senior research analyst at S&P Global Market Intelligence.
The Bipartisan Infrastructure Law that passed in November 2021 promises to bridge this digital divide, with $65 billion dedicated to expanding access to broadband internet to all Americans. Such government support, along with a number of other factors, have caused a spike in the demand for fiber products.
To understand the technology behind fiber-optic internet and how the market for fiber products is changing, CNBC visited Corning’s optical fiber and cable manufacturing facilities in North Carolina. Most famous as the maker of Gorilla Glass for iPhones, Corning is also the world’s largest producer of optical fiber by manufacturing capacity and market share, as well as the largest manufacturer of fiber cable in North America. In Q2 2022, Corning disclosed that the optical communications business was its largest segment by revenue, reaching sales of $1.3 billion.
spacer
OCEAN Internet Cables
spacer
The hidden network that makes the internet possible – Sajan Saini
TECHNOLOGY
The Global Fiber Optic Network Explained
As we scroll through Instagram or cue up another episode on Netflix, most of us give little thought to the hidden network of fiber optic cables that instantaneously shuttle information around the globe.
This extensive network of cables – which could stretch around the Equator 30 times – is the connective tissue that binds the internet, and thanks to our insatiable appetite for video streaming, it’s growing larger with every passing year.
Today’s video, by TED-Ed, explains how fiber optic cables work and introduces the next generation of cables that could drastically increase the speed of data transmission.
A Series of Tubes
The late Senator Ted Stevens drew laughter for describing the internet as a “series of tubes” in 2006, but as it turns out, most of the information moving around the world does, in fact, travel through a series of tubes. Undersea fiber optic tubes, to be exact.
The way this system functions is deceptively simple. Light, which is beamed into a fiber optic cable at a shallow angle, ricochets its way along the tube at close to light speed until being converted back into an electrical signal at its destination – generally a data center. To increase bandwidth further, some cables are able to carry multiple wavelengths concurrently.
Impressively, this simple method of bouncing light through a tube is what moves 99% of the world’s digital information.
The Glass Superhighway
Since the first undersea fiber optic cable, TAT-8, was constructed by a consortium of companies in 1988, the number of cables snaking across the ocean floor has risen dramatically. In fact, over 100 new cables will have been laid between 2016 and 2020, with a value of nearly $14 billion.
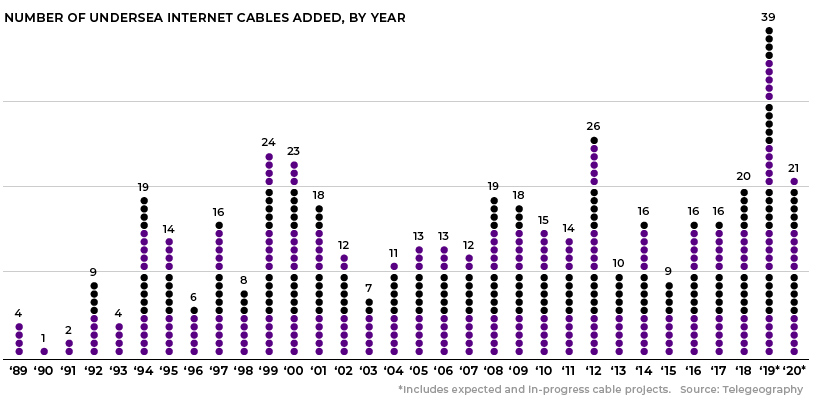
Increasing bandwidth requirements have transformed content providers from customers to cable owners. As a result, tech giants like Google and Facebook are taking a more active role in the expansion of the global fiber optic network. Google alone has at least five cable projects set for completion in 2019.
The Last Mile
Much like Amazon struggles with the “last mile” of deliveries, the transmission of digital information is much less efficient at the data center level, where servers are connected by traditional electric cables. These short-range cables are far less efficient than their fiber optic counterparts, losing half their running power as heat.
If this inefficient use of energy isn’t solved, internet-related activity could comprise a fifth of the world’s power consumption by 2030.
Thankfully, a related technology – integrated photonics – could keep the high-definition videos of the future streaming. Although the silicon wires used in integrated photonics do not guide light as effectively as fiber optics, the ultra-thin wires are far more compact. Photonic chips paired with burgeoning terahertz (THz) wireless communications could eventually form the backbone of a 6G network. Short-range THz signals would hitch a ride on silicon wires via tiny photonic chips scattered around population centers.
Before this efficient, high-capacity future is realized, researchers must first solve the puzzle of manufacturing photonic devices at scale. Once this method of data transmission hits the mainstream market, it could drastically alter the course of both computing and global energy consumption.
spacer
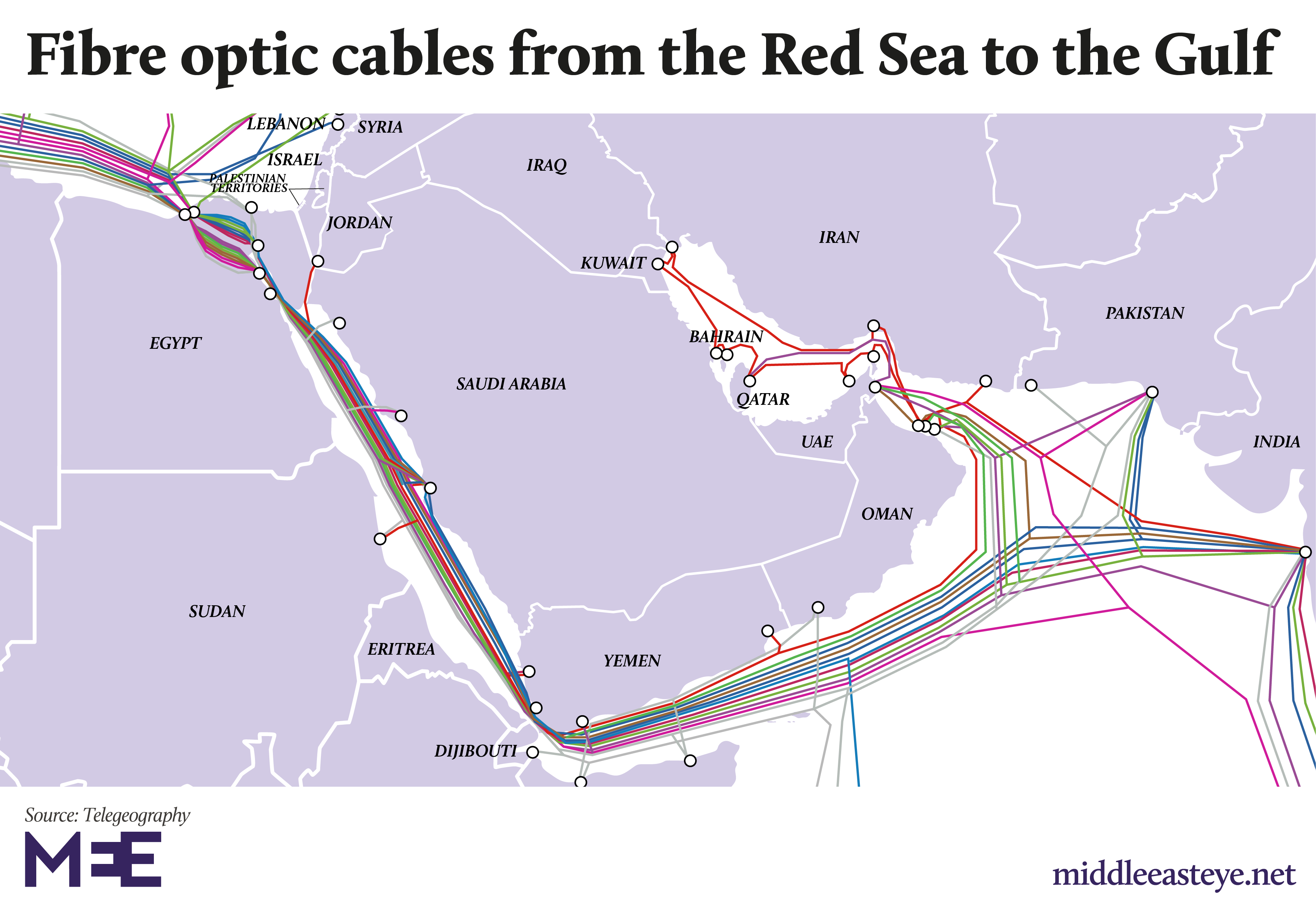
Red Sea cables: How UK and US spy agencies listen to the MiddleEast
An expanding network of undersea fibre optic cables from the Mediterranean to the Gulf has made surveillance of regional communications easier than ever

A view of the Strait of Tiran from Egypt’s Sharm el-Sheikh in 2014. The Red Sea is an important route for undersea cables (AFP)
The growth of Middle Eastern fibre optic cable networks has given Western signals intelligence agencies unprecedented access to the region’s data and communications traffic.
“There is no question that, in the broadest sense, from Port Said [in Egypt] to Oman is one of the greatest areas for telecommunications traffic and therefore surveillance. Everything about the Middle East goes through that region except for the odd link through Turkey,” said Duncan Campbell, an investigative journalist specialising in surveillance since 1975.
The Five Eyes, a signals intelligence (SIGINT) alliance of the US, the UK, Canada, Australia and New Zealand, has been snooping on the Middle East since the network was formed during the Second World War.
The key players are the US’s National Security Agency (NSA), and the UK’s Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), utilising both known and secret facilities in the region to collect data.
The Middle East is a hotbed of surveillance for obvious reasons: its strategic political-economic importance, the Arab-Israeli conflict, and political divisions between the allies of the Five Eyes and their adversaries, from militant groups to countries such as Iran and Syria.

While all conventional forms of surveillance are carried out, from airspace surveillance to tapping phone lines, the region is a strategic asset for mass surveillance due to the current routes of fibre optic cables.
“The importance of cables is still largely unknown by the average person. They think smartphones are wireless and it goes through the air but they don’t realise it is through cables,” said Alan Mauldin, research director at telecommunications research firm TeleGeography in Washington.
Spy agencies have tapped into fibre optic cables to intercept vast volumes of data, from phone calls to the content of emails, to web browsing history and metadata. Financial, military and government data also passes through cables.
Such intercepted data is sifted by analysts, while filters extract material based on the NSA and GCHQ’s 40,000 search terms – subjects, phone numbers and email addresses – for closer inspection.
“This physical system of fibre optic cables joins the major countries of the world and carries over 95 percent of international voice and data traffic. Given the importance of undersea cables, they are poorly protected by international law,” said Athina Karatzogianni, an academic researching the importance and regulation of undersea cables.
“They represent perhaps the most extreme example of states privatising critical infrastructure but failing to extend protection.”
Geostrategic cables
Between the Red Sea and Iran there are no terrestrial fibre optic cables crossing the Arabian peninsula. All internet traffic going from Europe to Asia either passes through the Caucuses and Iran, using the Europe Persia Express Gateway (EPEG), or via the far more congested Egyptian and Red Sea routes.
Egypt is a major chokepoint, handling traffic from Europe to the Middle East, Asia and Africa, and vice versa. The 15 cables that cross Egypt between the Mediterranean and Red seas handle between 17 percent to 30 percent of the world population’s internet traffic, or the data of 1.3 billion to 2.3 billion people.
Geography and politics has led to this particular set-up. “You cannot build a link through Syria or Iran due to the conflict and the political situation, and the war in Yemen takes out another terrestrial option, so [cables] take another path,” said Guy Zibi, founder of South African market research firm Xalam Analytics.
“There are only a few areas globally that are so highly strategic; the Red Sea is one of them, and in the African context, Djibouti.”
Most cables run under the sea, making the land crossing of Egypt more of an exception than the rule. Subsea cables are preferred as they are considered more secure, with greater vulnerability when cables hit land and then run terrestrially. “It is difficult to go under the sea and harm cables,” said Zibi.
The cables that run across Egypt and via the Suez Canal have logistical risks, such as breakages by anchors in the Suez’s shallow waters or from human interference.
“In 2013, three divers with hand tools cut the main cable connecting Egypt with Europe, reducing Egypt’s internet bandwidth by 60 percent,” said Karatzogianni.
The cables running through Egypt do not give the Egyptian state free rein to intercept data on behalf of the Five Eyes, however, despite the importance that President Abdel Fattah el-Sisi, a former director of military intelligence, and his son, Mahmoud, the deputy head of the General Intelligence Directorate (GID), place on mass surveillance of Egyptian citizens.
“The Egyptians are superbly placed to have access [to data on the cables], but are not considered a trustworthy or stable partner. It is not where you want to put slick high-end [surveillance] equipment,” said Campbell.
Despite its strategic importance, Egypt is not part of any wider SIGINT networks. The Five Eyes alliance has information-sharing arrangements in place with some European countries and Japan and South Korea, for example, to intercept data from Russia and China. The NSA also has a relationship with Sweden, because it is a landing point for all cable traffic from Russia’s Baltic region.
By contrast, the US has less formal information-sharing relationships with a number of countries in the Middle East region including Egypt, Israel, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Turkey and the UAE.
“The Egyptians have an intelligence-sharing agreement [with the US], but they are probably quite supine in the relationship, being after the money [from the cable operators] and some intelligence sharing, which is largely [from the US side], ‘here’s what you get’,” said Hugh Miles, founder of Arab Digest, in Cairo.
Secret tapping
The Five Eyes could be tapping cables in Egypt or its territorial waters, however. Documents leaked by Edward Snowden in 2013 refer to a clandestine NSA base in the Middle East called DancingOasis, also referred to as DGO.
“It is extremely secret. Significantly it was built without [the host] government knowing, which is an immense risk to the Americans,” said Campbell. “Where it is located is pure guesswork. Candidate one is Jordan, then Saudi Arabia, and three, Egypt. Geographically the only other place would be Oman, from where Britain covers the Gulf.”
The cables connecting Europe, Africa and Asia run across Egypt and then down the Red Sea to the Bab el Mandeb strait between Yemen and Djibouti. The cables heading east veer off towards Oman. To the west of the capital Muscat is a GCHQ surveillance site in Seeb, with the code name Circuit.
“It is very close to where the submarine cables come in. Virtually all cables take a landfall between Seeb and Muscat. How convenient is that?” said Campbell.
For internet traffic to be tapped going from Oman to Europe, “the best option would be ultra-secret taps in the sea,” he added.
The Snowden leaks revealed that subsea taps are carried out by a specially converted submarine, the USS Jimmy Carter.
“There is a high degree of suspicion that American or other countries’ submarines use subsea platforms to intercept cables,” said Campbell.
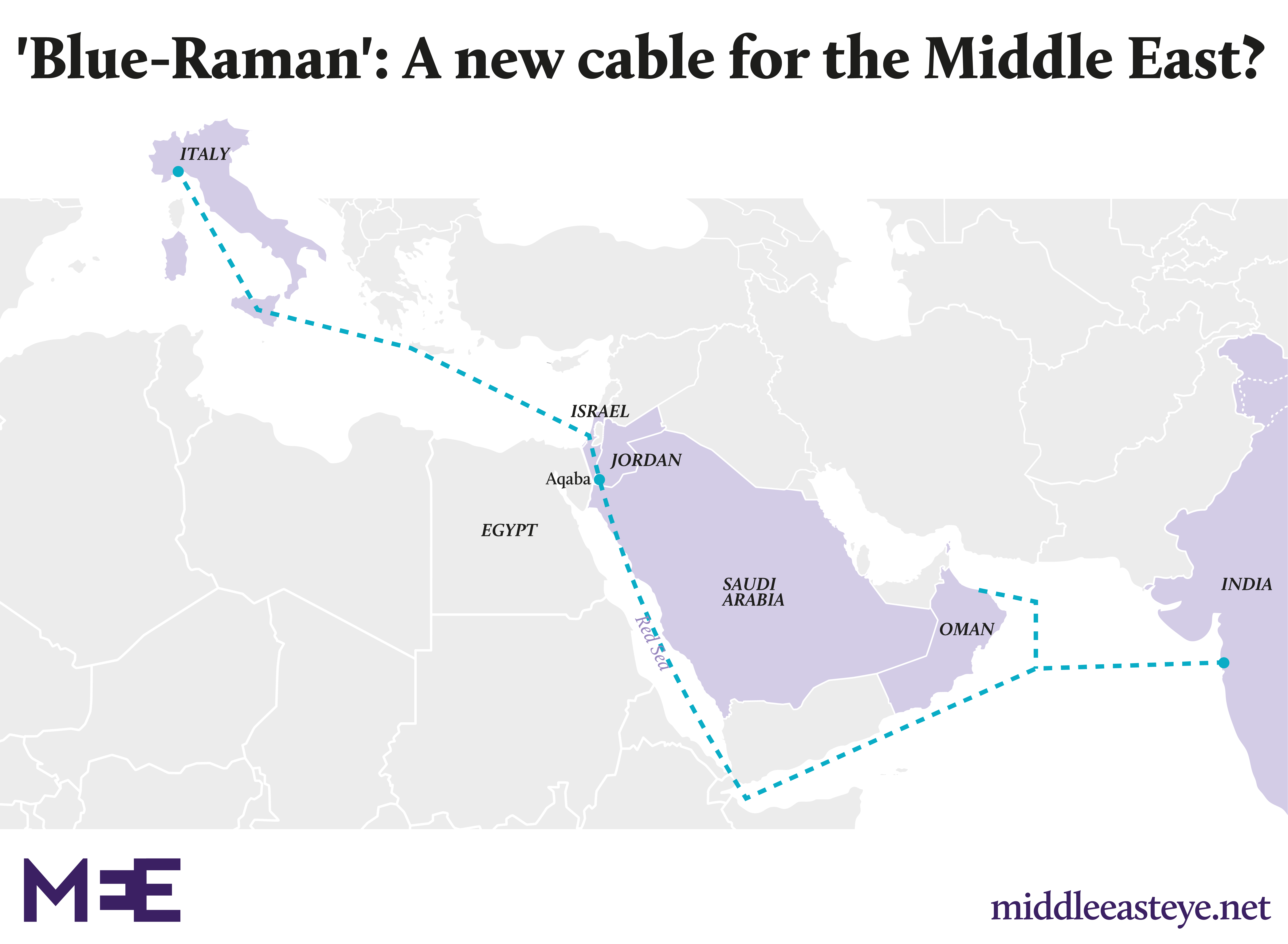
A new cable for the region?
Israel is another country with the technical capability to tap subsea cables in the region, according to Campbell, though it currently has no connections to Middle Eastern networks.
There are no cables that go beyond the two coastal landing points of Tel Aviv and Haifa, which are connected to continental Europe and Cyprus.
This could change if Google’s reported plans for its new “Blue-Raman” cable running from Europe to India through Israel, Jordan, Saudi Arabia and Oman come to fruition.
The cable is split in two, with the Blue part of the cable running from Italy to Aqaba on Jordan’s Red Sea coast. The Raman cable runs from the Jordanian port south to Mumbai.
“As it is a Google cable, they know how to secure everything end-to-end. They will have built into their business plan the landfall at or near Tel Aviv, and will factor in that the Israelis will copy all data at the landing point, and encrypt against them. That doesn’t mean they [Israel] won’t take the traffic and see what they can get,” said Campbell.
It is not clear if the Blue-Raman cable will go ahead, seemingly dependent on a normalisation agreement between Saudi Arabia and Israel.
Google did not respond to Middle East Eye’s queries about the reported project.
“If Saudi Arabia signs up to the deal with the Israelis, it will be a significant moment in geopolitics, where tech infrastructure – the fibre optic cable – becomes a facilitator for strategic collaboration between regional historical enemies,” said Karatzogianni.
This article is available in French on Middle East Eye French edition
spacer
How Fiber Optic Infrastructure is Paving the way for 5G
spacer
END GAME – 60 GHZ AND 5G
spacer
MYOFASCIAL SYSTEM: OUR INTERNAL FIBER OPTICS | SEAN MCCORMICK PODCAST
spacer
BIOTECH ANALYST KAREN KINGSTON UNVEILS THE COVID VACCINE 5G LINK + BIOSYNTHETIC AI NANOTECH
Biotech analyst Karen Kingston unveils the covid vaccine 5G link + biosynthetic AI nanotech
– Covid-19 injections contain NEUROWEAPONS embedded in Lipid Nanoparticels (LNP)
– Neurological weapons were hidden through Emergency Use Authorization cover-up
– Shocking patents confirm it’s all true (patent numbers shown)
– Transhumanism assault on humanity now under way, people becoming LESS human
– LNPs can be activated via 5G frequencies to achieve physiological changes
– Covid “vaccines” appear to be exotic tech INSTALLED in human hosts
– CCP-linked AI company named “national security threat” in USA
– 5G infrastructure to be exploited by AI embedded systems for surveillance
– Post-vaccine “biostructures” are self-assembling biosynthetic weapons
For more updates, visit: http://www.brighteon.com/channel/hrreport
spacer
COVID “TESTS” & “VACCINES” DELIVERING A HYBRID BIO/TECH WEAPON ACTIVATED BY 5G, FIBER OPTICS, LIGHT
https://rumble.com/c/Ezek34
Karen Kingston uncovers patents revealing “cognitive action” spike protein structures in vaccines
– More patents reveal shocking nature of “spike protein” structures in vaccines
– Hybrid structures demonstrate “cognitive action” capabilities
– Described in patents as “intelligent sensor platforms” that carry out instructions
– So-called “spike proteins” seen in electronic microscopy are actually these nanotech platform structures
– They are small enough to enter nervous system cells and alter their behavior
– More details on quantum dots used by the US Army, combined with carbon nanotubes
– See https://breakingdefense.com/2020/01/carbon-nanotubes-quantum-dots-army-thinks-very-small/
The information Kingston discussed is included in various articles on her Substack in a series titled ‘Dismantling Covid-19 Deceptions’. Below are links to documents discussed in the first 30 minutes of the video above:
(ALL LINKS WORKING CORRECTLY NOW–…..Ezek34)
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2012148684
https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/9e/bc/82/52d2a8e8c97ac2/US20130251618A1.pdf
https://karenkingston.substack.com/p/part-5-dismantling-the-covid-19-deceptions
https://karenkingston.substack.com/p/part-2-dismantling-the-deceptions
https://karenkingston.substack.com/p/part-4-dismantling-the-covid-19-story
https://www.bitchute.com/video/VQ82yqtbkqsv/
https://citizens.news/663687.html
https://expose-news.com/2022/10/20/biotechnology-experimentation-has-to-be-stopped/
https://citizens.news/663687.html
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/quantum-confinement-effect
spacer
What is 6G?
6G is the name for the sixth generation of cellular networks, which will deliver truly omnipresent wireless intelligence. Expected to become available early in the 2030s, the 6G research journey is already well underway.
The vision for 6G is built on the desire to create a seamless reality where the digital and physical worlds as we know them today have merged. This merged reality of the future will provide new ways of meeting and interacting with other people, new possibilities to work from anywhere and new ways to experience faraway places and cultures.
By delivering ever-present intelligent communication, 6G will contribute to the creation of a more human-friendly, sustainable and efficient society.
IMAGINE POSSIBLE: 6G Fragments of Time
Watch the video on ericson.com ![]()

Introducing the cyber-physical continuum
6G will make it possible to move freely in the cyber-physical continuum, between the connected physical world of senses, actions and experiences, and its programmable digital representation.
The cyber-physical continuum of 6G includes the metaverse as it is typically understood – a digital environment where avatars interact in a VR/AR world – and goes further, providing a much closer link to reality. In the cyber-physical continuum, it will be possible to project digital objects onto physical objects that are represented digitally, allowing them to seamlessly coexist as merged reality and thereby enhance the real world.
spacer
XR is the future of mobile computing. We are making mobile XR a reality.Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term encapsulating Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Mixed Reality (MR), and everything in between. Although AR and VR offer a wide range of revolutionary experiences, the same underlying technologies are powering XR. Qualcomm’s vision for XR is sleek headsets that will transform everyday consumer experiences and many market verticals from industrial manufacturing and healthcare to education and retail. |
||
|
Future networks will be a fundamental component for the functioning of virtually all parts of life, society, and industries, fulfilling the communication needs of humans as well as intelligent machines. As accelerating automatization and digitalization continue to simplify people’s lives, the emerging cyber-physical continuum will continuously improve efficiency and ensure the sustainable use of resources.
Countless sensors will be embedded in the physical world to send data to update the digital representation in real time. Meanwhile, functions programmed in the digital representation will be carried out by actuators in the physical world. The purpose of the 6G network platform is to provide intelligence, ever-present connectivity and full synchronization to this emerging reality.
Cyber Physical Continuum

Read the white paper: 6G – connecting a cyber-physical world
What will the world be like with 6G?
We envision a connected and sustainable physical world that is both digitalized and programmable, where humans are supported by intelligent machines and the Internet of Senses.
Examples of important 6G use cases include e-health for all, precision health care, smart agriculture, earth monitor, digital twins, cobots and robot navigation. These use cases can be sorted into three broad use case scenarios: the Internet of Senses, connected intelligent machines, and a connected sustainable world.
spacer
Connected Sustainable World – Future Technologies

In the Internet of Senses scenario, the immersive communication of 6G will deliver the full telepresence experience, removing distance as a barrier to interaction. Extended reality (XR) technology with human-grade sensory feedback requires high data rates and capacity, spatial mapping with precise positioning and sensing, and low latency end-to-end with edge cloud processing. One example will be the ubiquitous use of mixed reality in public transport, offering separate virtual experiences for each passenger, enabling them to run virtual errands, get XR guidance and have games overlaid on the physical world.
Personal immersive devices capable of precise body interaction will allow access to experiences and actions far away to better support human communication needs. At the same time, 6G networks will also add completely new communication modes with strict control over access and identities.
Connecting the digital and physical worlds will require countless sensors that send data to update the digital representation in real time. Actuators in the real world will carry out functions that are programmed in the digital representation. The 6G network platform will provide intelligence, ever-present connectivity and full synchronization in a cyber-physical continuum. The result? Full support for connected intelligent machines, the Internet of Senses, and a connected sustainable world.
spacer
6G roadmap: Growing from 5G to 6G
It is too early yet to define a detailed roadmap for 6G. Research into new technology areas is ongoing in parallel with the evolution of 5G. Learnings from live 5G networks and interactions with the user ecosystems will continuously feed into the research, standardization and development of 6G.

Evolution and long-term horizon – 5G Advanced and 6G
6G will build on the strengths of 5G, but it will also provide entirely new technology solutions. Around 2030 is a reasonable time frame to expect the very first 6G networks to appear.
By that time, society will have been shaped by 5G for 10 years, with lessons having been learned from 5G deployment, and new needs and services appearing. Even with the built-in flexibility of 5G, we will see a need for expanding into new capabilities. This calls for further evolution – following the pull from society’s needs and the push from more advanced technological tools becoming available – that must be addressed for the 6G era when it comes.
5G New Radio (NR) and 5G Core (5GC) evolution is continuing in 3GPP toward 5G Advanced, to ensure the success of 5G systems globally and to expand the usage of 3GPP technology by supporting different use cases and verticals. Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (AI/ML ) will play an important role in 5G Advanced systems, in addition to other technology components, to provide support for extended reality (XR), reduced capability (RedCap) devices, and network energy efficiency.
|
Ericsson Reduced Capability (RedCap) is a new RAN software solution that enhances existing 5G use cases and enables new ones (mid-tier use cases) for devices such as smartwatches, other wearables, and industry sensors by lowering complexity and extending battery life.
|
spacer
While Ericsson 5G networks already support AI/ML and XR use cases and requirements in an energy-efficient manner, it is essential to enhance the 5G standards to improve multi-vendor support and provide better device and network cooperation. The 5G Advanced standardization is an important step in the evolution of cellular wireless access toward 6G.
The improved capabilities of 5G Advanced include enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low latency communication (URLLC), and massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC), all of which serve as important stepping stones leading toward the future 6G system.
spacer
QUANTUM UPLOAD OF BRAIN CLOUD RECORDINGS. SHOCKING NEW PCR TECHNOLOGY!!!!!
Our host Challis goes in on
Brain to Cloud Tech. Also how
We are not immune from the new…
Sources:
https://www.BrainLatam.com
https://www,FrontiersIn.org (2019)
spacer